Research Gallery > Planetary Sciences
Research Gallery
Planetary Sciences
| Number of cometary nuclei required to sustain a population of JFCs in steady state. |
|
Image Credit: M. A. Muñoz-Gutiérrez
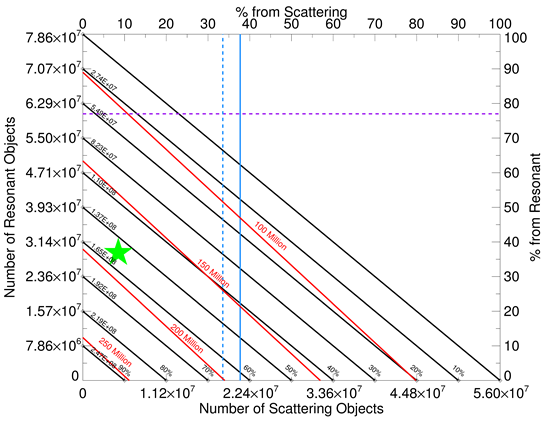
A figure representing the different possible combinations of the contributions of each of the three populations of the Kuiper belt (Classical, Resonant, and Scattering), to the total Jupiter Family Comet (JFC) production.
|
| Each point of the lower-left triangle represents one possible combination. The fractional contribution of the Scattering and Resonant populations are presented in the upper and right axes respectively, while the remaining fraction, corresponding to the Classical population, is presented in the inner part of the lower axes; the corresponding number of particles required to produce such fractions are presented in the outer lower axis, the outer left axis and the inner left axis for the Scattering, Resonant, and Classical populations, respectively. The red diagonal lines correspond to the sum of the three populations, or the total reservoir of cometary nuclei, the dashed and solid blue lines correspond to the uncorrected and corrected estimation of the scattering population (as estimated by Greenstreet et al. 2019), the dashed purple line corresponds to the uncorrected resonant population (as estimated by Greenstreet et al. 2019), their corrected Resonant population, as well as their Classical population lie outside the area of the �figure. Finally, the green star represents our preferred distribution as estimated from the L7 particle distribution. |
 asiaa.sinica.edu.tw Media Request: epo
asiaa.sinica.edu.tw Media Request: epo asiaa.sinica.edu.tw
asiaa.sinica.edu.tw 
