|
圖片來源: Algaba, Nakamura, Asada, Lee (2017), ApJ, 834, 65
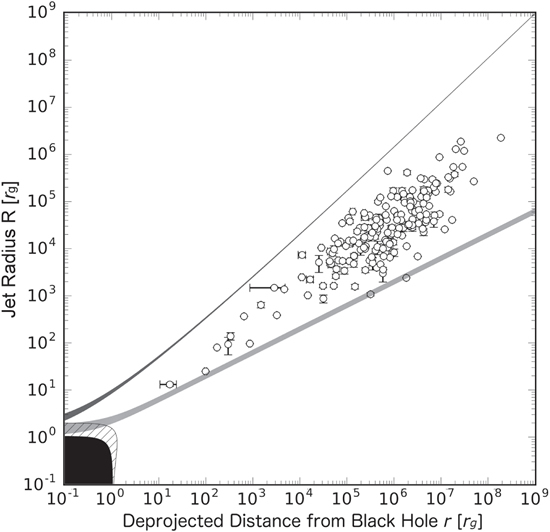
In the current paradigm, it is believed that the compact VLBI radio core of radio-loud AGNs represents the innermost upstream regions of relativistic outflows. These regions of AGN jets have generally been modeled by a conical outflow with a roughly constant opening angle and flow speed. Nonetheless, some works suggest that a parabolic geometry would be more appropriate (M87: Asada & Nakamura 2012, Nakamura & Asada 2013; NGC 6251: Tseng, Asada, Nakamura et al. 2016; 3C 273: Akiyama, ..., Nakamura et al. 2018; NGC4261: Nakahara, ..., Nakamura et al. 2018; Cyg-A: Nakahara, ..., Nakamura et al. 2018, ApJ submitted). Here we compile multi-frequency core sizes of archival data to investigate the typically unresolved upstream regions of the jet geometry of a sample of 56 blazars. Data combined from the sources considered here are?not consistent with the classic picture of a conical jet starting in the vicinity of the super-massive black hole (SMBH), and may exclude a pure parabolic outflow solution, but rather suggest an intermediate solution with quasi-parabolic streams, which are frequently seen in numerical simulations. Our result suggests that the conical jet paradigm in AGNs needs to be re-examined by millimeter/sub-millimeter VLBI observations.
|
 asiaa.sinica.edu.tw 媒體連絡: epo
asiaa.sinica.edu.tw 媒體連絡: epo asiaa.sinica.edu.tw
asiaa.sinica.edu.tw