Research Gallery > Interstellar and Circumstellar Medium
Research Gallery
Interstellar and Circumstellar Medium
| Effects of grain size distribution on the interstellar dust mass growth |
|
Image Credit: Hiroyuki Hirashita and Tzu-Ming Kuo
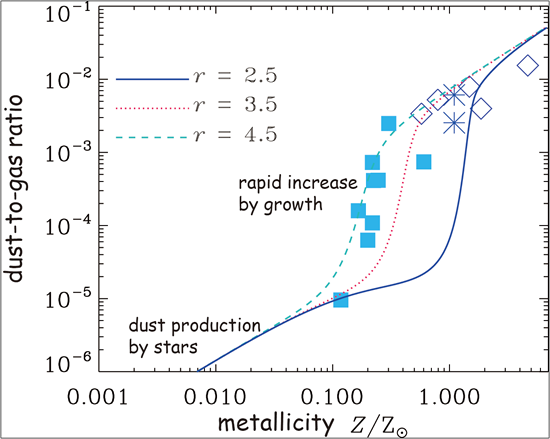
The figure above demonstrates how the dust-to-gas ratio in a galaxy evolves with increasing metallicity. In the low-metallicity regime, the dust is predominantly supplied by stars, so the dust-to-gas ratio increases in proportion to metallicity. Above a certain metallicity, the dust-to-gas ratio rapidly increases because the dust growth in the interstellar medium becomes more and more important, because interstellar dust growth occurs efficiently in metal-rich interstellar environments. The rapid increase is indeed consistent with the observational data of nearby galaxies.
|
| ASIAA researchers Hiroyuki Hirashita and Tzu-Ming Kuo calculated the evolution of dust content in galaxies by taking into account these two dust production processes, as well as dust destruction by supernova shocks. Because dust grains are composed of metals, the relation between metallicity (fraction of metals in gas) and dust-to-gas ratio (fraction of dust to gas) is useful to examine the evolution of dust content in a galaxy. The metallicity of a galaxy increases over time, due to the built up of nucleosynthesis products from stellar ejecta into the interstellar medium and is an indicator of the evolutionary stage of a galaxy. |
 asiaa.sinica.edu.tw Media Request: epo
asiaa.sinica.edu.tw Media Request: epo asiaa.sinica.edu.tw
asiaa.sinica.edu.tw 