Research Gallery > The Theoretical Astrophysics (Theory)
Research Gallery
The Theoretical Astrophysics (Theory)
| Comparison with submillimeter galaxy surveys |
|
Image Credit: Aoyama, Hirashita, et al. 2019
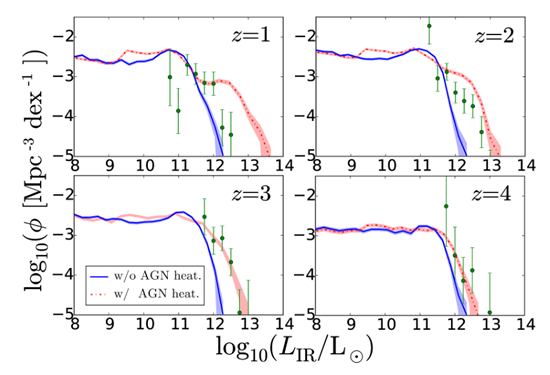
We post-processed our cosmological hydrodynamic simulation with a simple dust emission model and calculated the infrared luminosity functions at redshifts z = 1–4 (Aoyama et al. 2019). We compare the calculated infrared (dust-emission) luminosity functions with the data points derived from the JCMT large project in our institute (PI: Wei-Hao Wang; Lim et al., in preparation). We broadly reproduced the observation data. The excess of the observational data points at extremely bright IR luminosity could be reproduced if we include additional heating by active galactic nuclei (AGNs).
|
| Simulations of structure formation in the Universe (cosmological simulations) are the backbone in understanding galaxy formation and evolution. Considering the collaboration with the observational groups in our institute, we are focusing on the prediction on the dust properties in galaxies at various redshifts (z ~ 0–4; Aoyama, Hirashita, et al. 2019). We post-processed our simulation with a simple dust emission model, and compared it with the galaxy sample in our JCMT project (STUDIES; PI: Wei-Hao Wang). |
 asiaa.sinica.edu.tw Media Request: epo
asiaa.sinica.edu.tw Media Request: epo asiaa.sinica.edu.tw
asiaa.sinica.edu.tw 
